3D Particle Tracking
Tracking of the three-dimensional position of actively motion-controlled magnetic micro- and nano-particles over flat surfaces
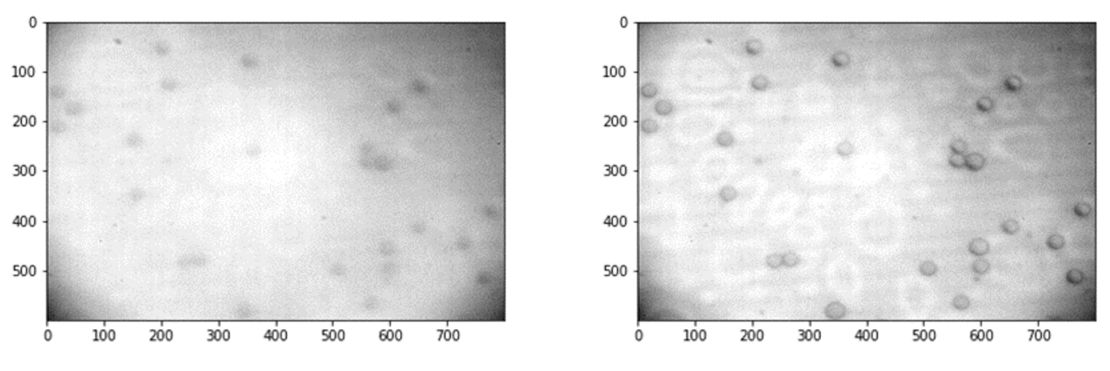
Typically, magnetic micro- and nano-particles immersed in a liquid in lab-on-chip systems are moving over a surface in a distance determined by the equilibrium of the acting forces between particle and chip-surface through the liquid. If these forces do change also the equilibrium distance will change. Up to now most of the motion analysis is carried out by determining the particles’ 2D positions as functions of time only, however, a determination also of the height over the substrate would allow a sensitive detection of modified forces by the change of the equilibrium particle-substrate distance, e.g. induced by particle coverage with an analyte. Here we try to develop an AI-based software for such a 3D tracking, exploiting the changing optical contrast of the videos, when particles move in different heights with respect to the focal plane of the microscope used to observe the particles.
Relevant Publications
- Three-dimensional close-to-substrate trajectories of magnetic microparticles in dynamically changing magnetic field landscapes. . In Scientific Reports, 12(1), p. 20890-. 2022.
- AdaPT: Adaptable particle tracking for spherical microparticles in lab on chip systems. . In Computer Physics Communications, 262, p. 107859. Elsevier BV, 2021.
- Transport Efficiency of Biofunctionalized Magnetic Particles Tailored by Surfactant Concentration. . In Langmuir, 37(28), pp. 8498–8507. 2021.
- AI-Based On The Fly Design of Experiments in Physics and Engineering. . In Workshop on Self-Improving System Integration. 2021.
- Translatory and rotatory motion of Exchange-Bias capped Janus particles controlled by dynamic magnetic field landscapes. . In Scientific Reports. Nature Publishing Group, 2021.
- Directed Magnetic Particle Transport above Artificial Magnetic Domains Due to Dynamic Magnetic Potential Energy Landscape Transformation. . In ACS Nano, 9(7), pp. 7323–7331. 2015.
